先上流程图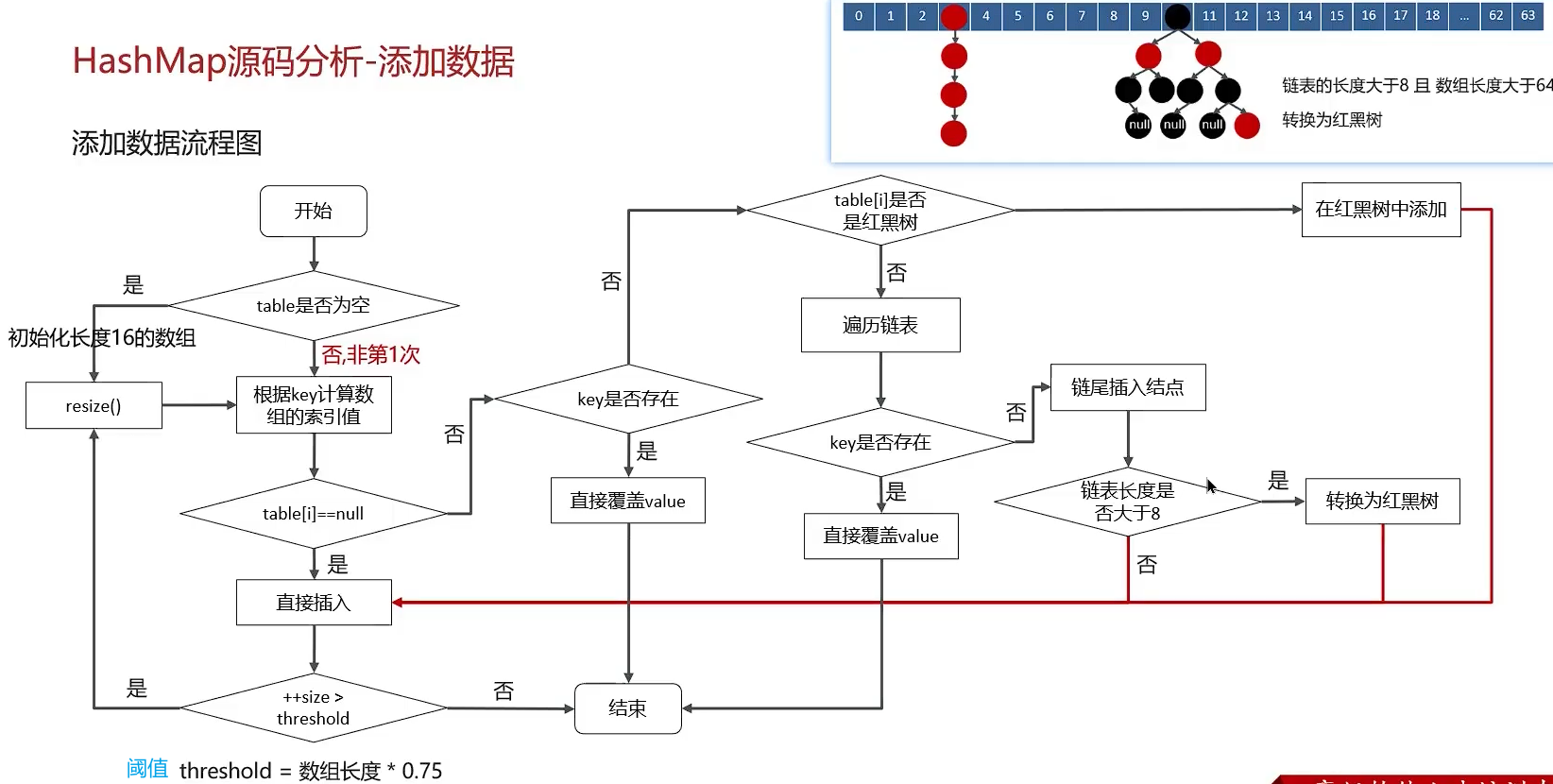
基本过程
- 判断键值对 table 数组(存数据的) 是不是空的,如果是需要进行初始化扩容 resize 为 16 大小,且阈值为 12
- 如果 table 非空,根据 key 进行哈希运算得到在数组中的(桶)索引,判断该索引的节点是不是空的,如果是空的则直接插入;(
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);)是新增节点,而不是赋值。
- 调用 put 方法时会调用底层的 putVal 方法
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } - 可以看到确实使用 hash 函数计算 key 对应的索引
- 如果该索引的节点不为空,则判断该位置 table[i]存的是不是红黑树节点
- 是红黑树节点:直接按照红黑树的插入方式插入该节点
- 不是红黑树节点:遍历链表
遍历链表时,如果和当前待插入节点 key 一样的链表节点存在,则直接覆盖 value;如果不同则在尾部插入新节点;
拓展:Jdk 8 之后采用尾插法,之前采用头插法, 参考:HashMap拉链法可能出现的问题
链表新增节点后,需要判断当前链表节点值是否超过了 8 个,如果超过,需要将该链表转换为红黑树;
最后节点插入完毕,判断当前数组中所有节点数是否大于阈值 threshold,如果大于还需要最后调用一次 resize ()进行扩容;
扩容过程参考:HashMap扩容
最后附上 putVal 完整源码
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}


